
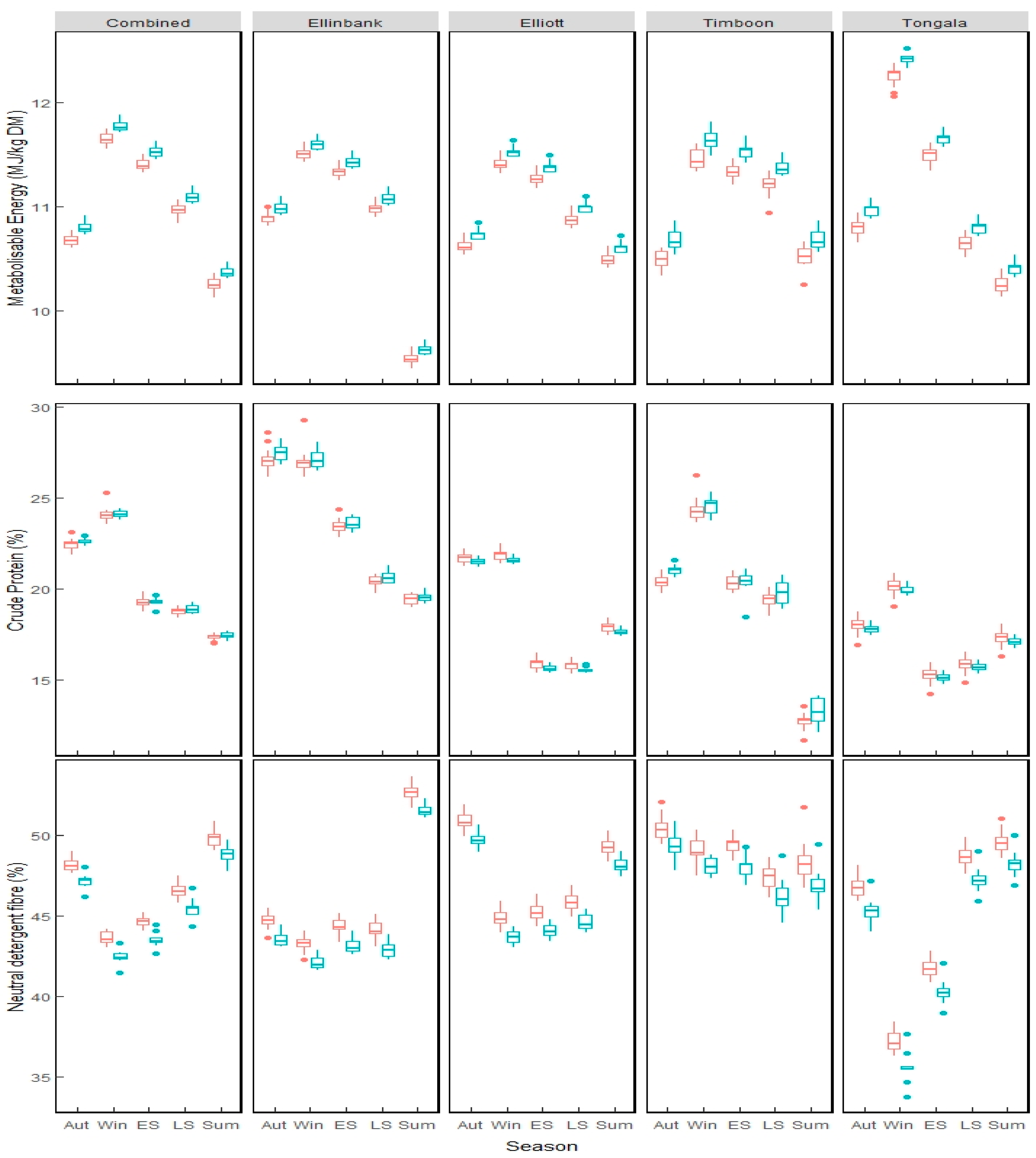
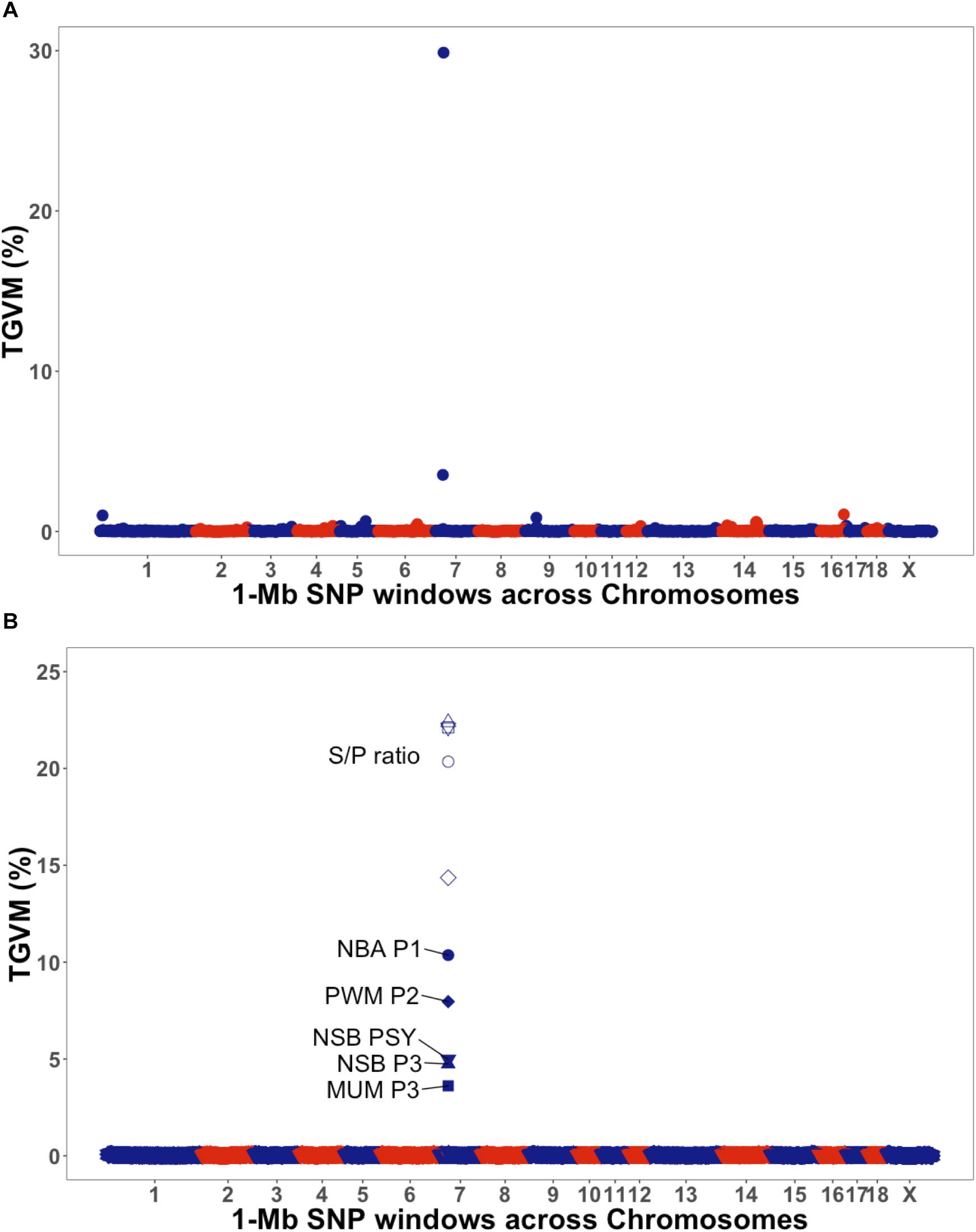
In both breeds, all nonlinear models fitted the data well, with an average coefficient of determination (R 2) of >0.98. Biologically relevant variables were estimated for each lamb from modified versions of the logistic, Gompertz, Richards, and exponential models, and from linear regression. Live BW records (n = 7559) from 240 Texel and 231 Scottish Blackface (SBF) lambs weighed at 2-wk intervals were modeled. When covariates are present in the model, the LSMEANS statement produces means which are adjusted for the average value of the specified covariate(s).This study compared the use of various models to describe growth in lambs of 2 contrasting breeds from birth to slaughter. The exact difference between MEANS and LSMEANS becomes more obscure with increasingly complex treatment arrangements and experimental designs. There is no inherent structure implied by the MEANS statement. LSMEANS is the proper choice here because it imposes the treatment structure of factor A on the calculated mean. Thus, when the data includes missing values, the average of all the data will no longer equal the average of the averages. Note that the second level of factor A at rep 1 is now deleted and hence the sums and means are updated to reflect this change. Suppose the data were revised as follows: If we delete a data point however, the results will change. Since the data were balanced the two methods produced the same result. The LSMEANS statement would use a linear combination of the estimated factor A effects, which in this case are the factor A means, a., Means for the 3 levels of factor A (a.) are given below each respective column.Ī MEANS statement would calculate the overall mean of factor A by summing all 9 This data set has a factor A with 3 levels (1, 2, & 3) with 3 reps of each. The following example illustrates the similarity and difference between theses two methods in balanced and unbalanced data. LSMEANS are also used when a covariate(s) appears in the model such as in ANCOVA (See handout # 4). In such a case the LSMEANS are preferred because they reflect the model that is being fit to the data.

When missing values do occur, the two will differ.
In the case where the data contains NO missing values, the results of the MEANS and LSMEANS statements are identical. Of the estimated effects (means, etc) from a linear model. LSMEANS - Least Squares Means can be defined as a linear combination (sum) They are also referred to as arithmetic means and they are based on MEANS - These are what is usually meant by mean (average) and are computedīy summing all the data points and dividing by the total # of points. In some cases they are equivalent and at other times LSMEANS are more appropriate. Statistical Programs: SAS Workshop - LSMEANS SAS Work Shop - GLMĪ common question asked about GLM is the difference between the MEANS and LSMEANS statements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
